Hello 👋
R
Pronounced /’Arrrgh/

GIPHY
Why R?
Because it’s the best!
End of presentation.

Why R?
R is a free and open source software environment for statistical computing and graphics
There are 20000+ available packages on CRAN
The R community is pretty cool
Why R(chaeology)?
Seems to be the most popular
Why RStudio?
RStudio is an integrated development environment (IDE) specifically for R
It provides a bunch of extra features to make using R a delight!
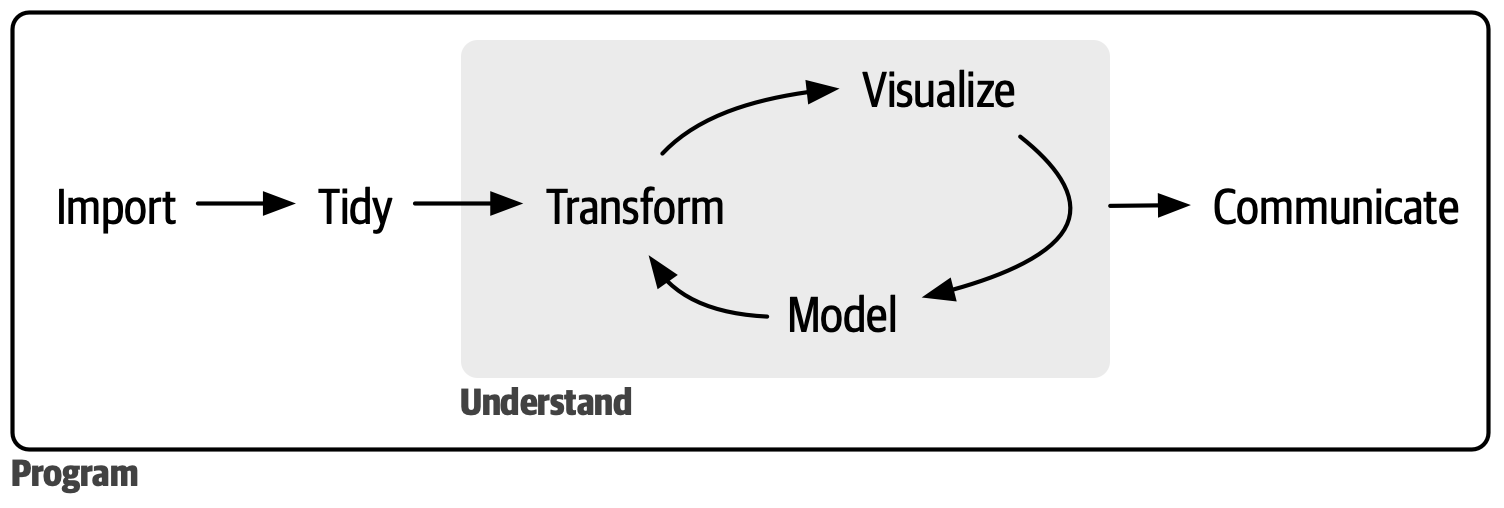
tidyverse
The tidyverse is a collection of R packages sharing the same data science philosophy
It provides a nice workflow for cleaning, visualising, and transforming data
Aspects of ‘base R’ will also be covered
About the materials
It is not enough to cover all important topics.
It is enough to teach you how to find answers and implement them yourself.

The datasets: Sheep Astragali
Sheep astragulus morphology from Iron Age Eastern Mediterranean.
nmar79. (2023). nmar79/Med_Sheep_Astragals: v0.1 (v0.1). Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10276147
The datasets: Sheep Astragali
| column | description |
|---|---|
| specID | Specimen ID |
| Taxon | Taxon |
| Site | Site code: DOR = Dor; KSN = Keisan; ABM = ABM (see group) |
| Zone | Zone: Coastal, inland, or Cyprus |
| Period | Time period: IA2 = Iron age; PER = Persian |
| group | Dor = southern Levant sample Iron Age 2 Tel Dor; Keisan = southern Levant sample Iron Age 2 and Persian Tell Keisan; southern Levant sample ABM = Iron Age 2 Abel Beth Maacah; LTD = Cypriot sample from Archaic-Classical Lingrin tou Digeni |
| GLl | Greatest length lateral astragalus measurement |
| Bd | Greatest breadth of distal end astragalus measurement |
| Dl | Greatest depth lateral astragalus measurement |
The datasets: Kiwulan Burials
Burial data from northeastern Taiwan ranging from the Iron Age through the European colonization period.
Li-Ying Wang & Ben Marwick, (2021). Compendium of R code and data for “A Bayesian networks approach to infer social changes from burials in northeastern Taiwan during the European colonization period”. Accessed 23 Aug 2021. Online at https://osf.io/xga6n/
The datasets: Kiwulan Burials
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Layer | Layer of the grave. 1 = Upper culture layer; 2 = Lower culture layer. |
| ID | Unique identifier of burials |
| Burial_axis | Not sure. Not relevant |
| Degree_axis | Not sure. Not relevant |
| Condition | Condition of the burial. 1 = complete; 2 = partial disturbed; 3 = severe disturbed; 4 = unidentified. |
| Gender | Biological sex of the skeletal remains. 1 = Male; 2 = Probable Male; 3 = Female; 4 = Probable Female. |
| Age | Age-at-death of the skeletal remains. 1 = infant (0-2 years); 2 = child (3-12 years); 3 = teenager (12-20 years); 4 = young adult(20-35 years); 5 = middle adult (35-50 years); 6 = old adult (50+); 7 = adult (20+); 8 = approximate adult |
| Length | Length of burial |
| Width | Width of burial |
| Height | Height of burial |